Project 5: Realtime (Algo)
You can find the handout for this project here. Please skim the handout before your Algo Section!
You may look through the questions below before your section, but we will work through each question together, so make sure to attend section and participate to get full credit!
Please read the project handout before going to algo section and working on these questions!
Projection Matrices
In lecture, we learned the two matrices that describe the camera: view and projection. In Ray, you learned how to generate a view matrix from a position, look, and up vector. In the Realtime projects, you will explore the concept of a projection matrix which covers the geometry of a view frustum!
Visuals
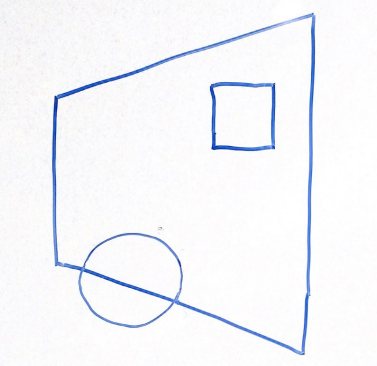
For the above scene in a 2D frustum, which of the following options best represents the same scene after being projected into clip space via a perspective projection? Why?
Think through this one on your own before discussing with your group!
Option 1 | Option 2 |
|---|---|
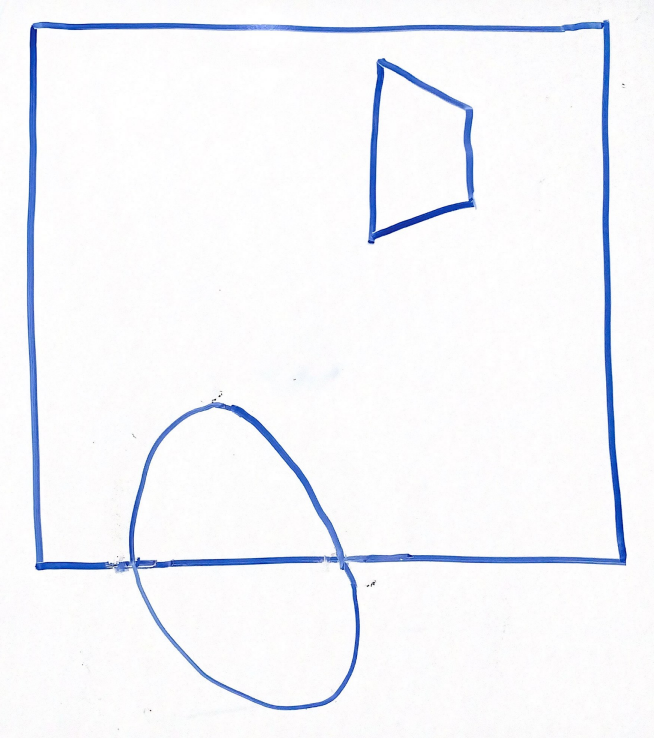 | 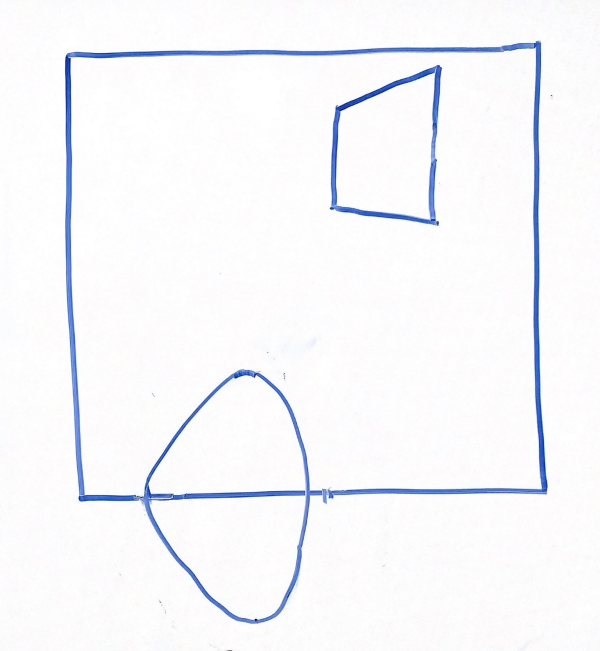 |
Option 3 | Option 4 |
|---|---|
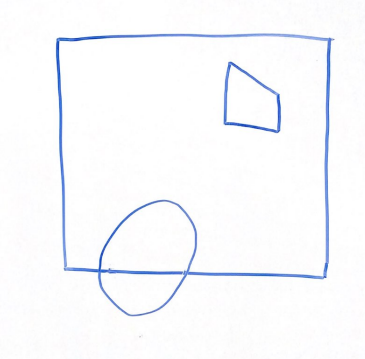 | 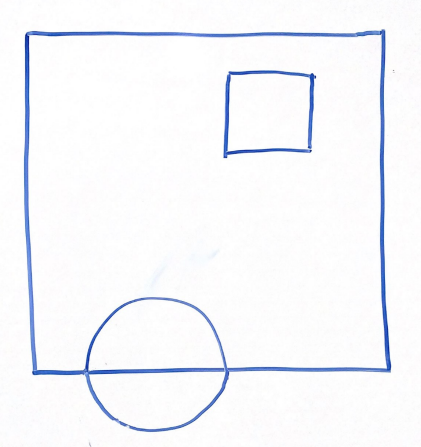 |
Scaling & Unhinging
Get together with a group and discuss the scaling and unhinging matrices. Explain why they are useful and how they interact with one another. How do they fit into the Realtime Pipeline?
Converting to OpenGL Space
The matrix below is multiplied on the left side of the two matrices above to convert to OpenGL's expected space. What are the x, y, and z limits in OpenGL's clip space and what is this doing to our previous projection to convert it to these limits?
Discuss the different components of this matrix with your group, and be prepared to explain your answers to the TA.
Camera Rotation
How would you compute the matrix for a rotation of 90 degrees about the axis
Once you have an idea of what to do, we recommend working through the math as a group!
Vertex Attributes
Vertex Buffer Format
Using
Don't get too caught up in the details—there may be multiple correct answers here... Have your group draw out the result on the whiteboard!
Vertex Arrays
For each attribute above (position, color, and texture coordinate), please provide the stride and offset (pointer) in bytes using size_of(GLfloat). (Assume GL_FLOAT)
| Stride | Offset | |
|---|---|---|
| Position | ||
| Color | ||
| Texture Coordinates |
Fill in the table above on the whiteboard. Note that your answers here may vary depending on how you answered the previous question
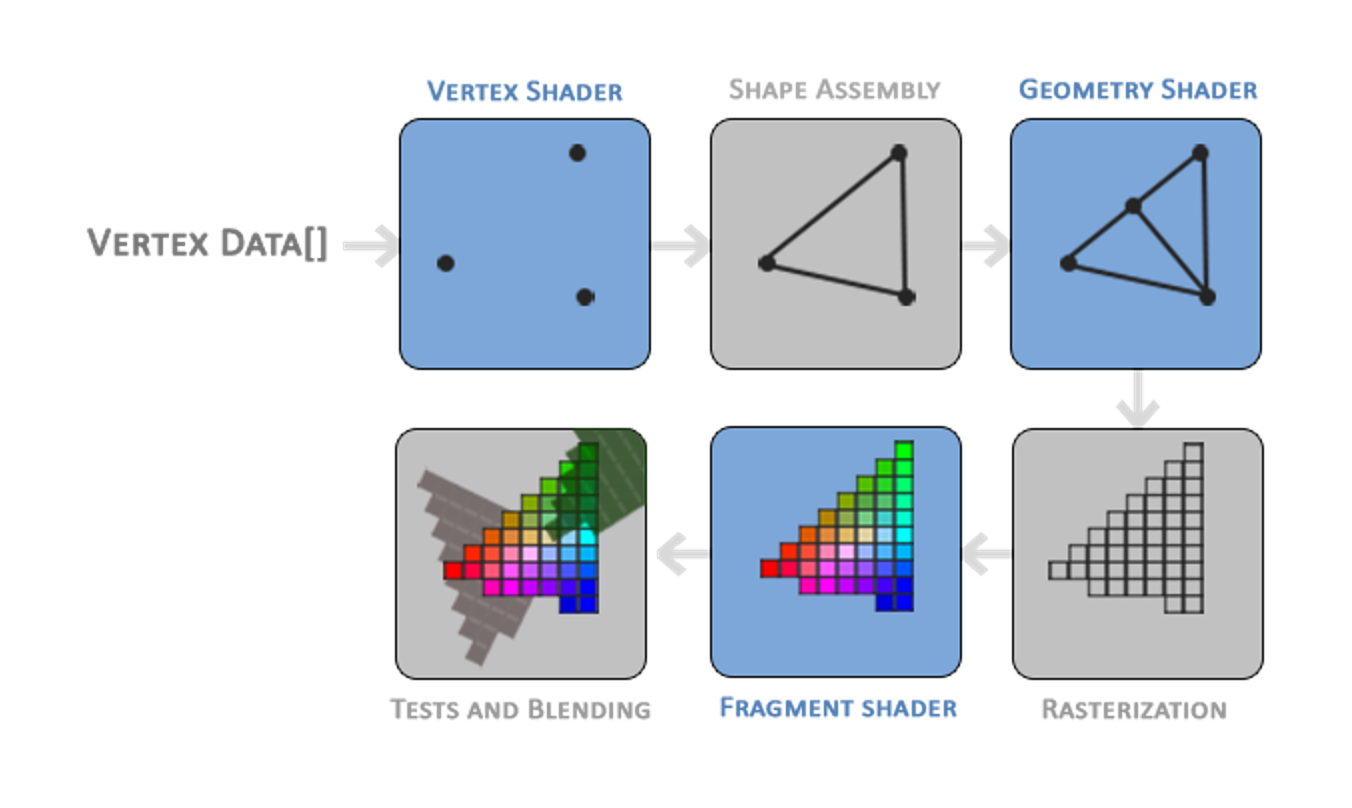
Realtime Pipeline
Conceptual Understanding
As a group, discuss how the concepts from Labs 8-10 synthesize in the Realtime Pipeline. Looking at the pipeline above, what are vertices, what are fragments and how do vertices and fragments become triangles? More specifically, how do the concepts of Trimeshes, VAOs / VBOs, and Shaders come together to create a final image in the OpenGL pipeline? You may want to refer to the pipeline diagram above to help guide your discussion. You answer shouldn't be too specific, but should demonstrate a high-level understanding of how these concepts interact.
Once your group comes to a consensus, share your answer with the TA.
Shader Programs
We can perform the same types of computation in both fragment and vertex shader. For this problem, compare the performance considerations associated with applying coordinate transforms in the vertex shader vs. the in fragment shader.
Think on Your Own: If we are drawing 1 triangle which covers exactly 50% of the pixels on an 1280 x 720 image, is it more efficient to compute an operation in the vertex shader or the fragment shader?
Now as a Group: Discuss why this is the case. Exactly how much more efficient does this computation become? In addition, please come up with an example of a computation that must be performed in the fragment shader.
Program Analysis
Erroneous Code
Consider the following initializeGL pseudo-code:
create VBO
bind VBO
fill VBO with data
unbind VBO
create VAO
bind VAO
set VAO attributes
unbind VAO
What would be the issue if a student tries calling glDrawArrays to draw their VAO in paintGL?
How could you change this pseudo-code to remove the error?
It may help to refer to lecture if you get stuck here!
Predict the Render
Given a VBO filled with data from an std::vector<GLfloat> of size 18, and VAO attribute code of:
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(GLfloat), nullptr);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(GLfloat), reinterpret_cast<void *>(3 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
How many vertices and how many triangles are described in the VBO/VAO pair?
If the VAO attribute code was changed to:
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(GLfloat), nullptr);
How many vertices and how many triangles are now described in the VBO/VAO pair?
Once you've answered both parts, check your understanding with the TA.
Realtime vs. Ray
Recursive Reflections
Why do you think we are not implementing recursive reflections in this assignment? There are many correct answers here! Discuss with your group, and consider the limitations of OpenGL in comparison to our earlier assignments.
Differences
Apart from recursive reflections, what are the advantages to using offline rendering as opposed to realtime rendering? What are the advantages to using realtime rendering as opposed to offline? Talk through some advantages of each side and share them with your TA.
Submission
Algo Sections are graded on attendance and participation, so make sure the TAs know you're there!