Project 4: Antialias (Algo Answers)
You can find the handout for this project here. Please skim the handout before your Algo Section!
You may look through the questions below before your section, but we will work through each question together, so make sure to attend section and participate to get full credit!
Discrete 2D Convolution
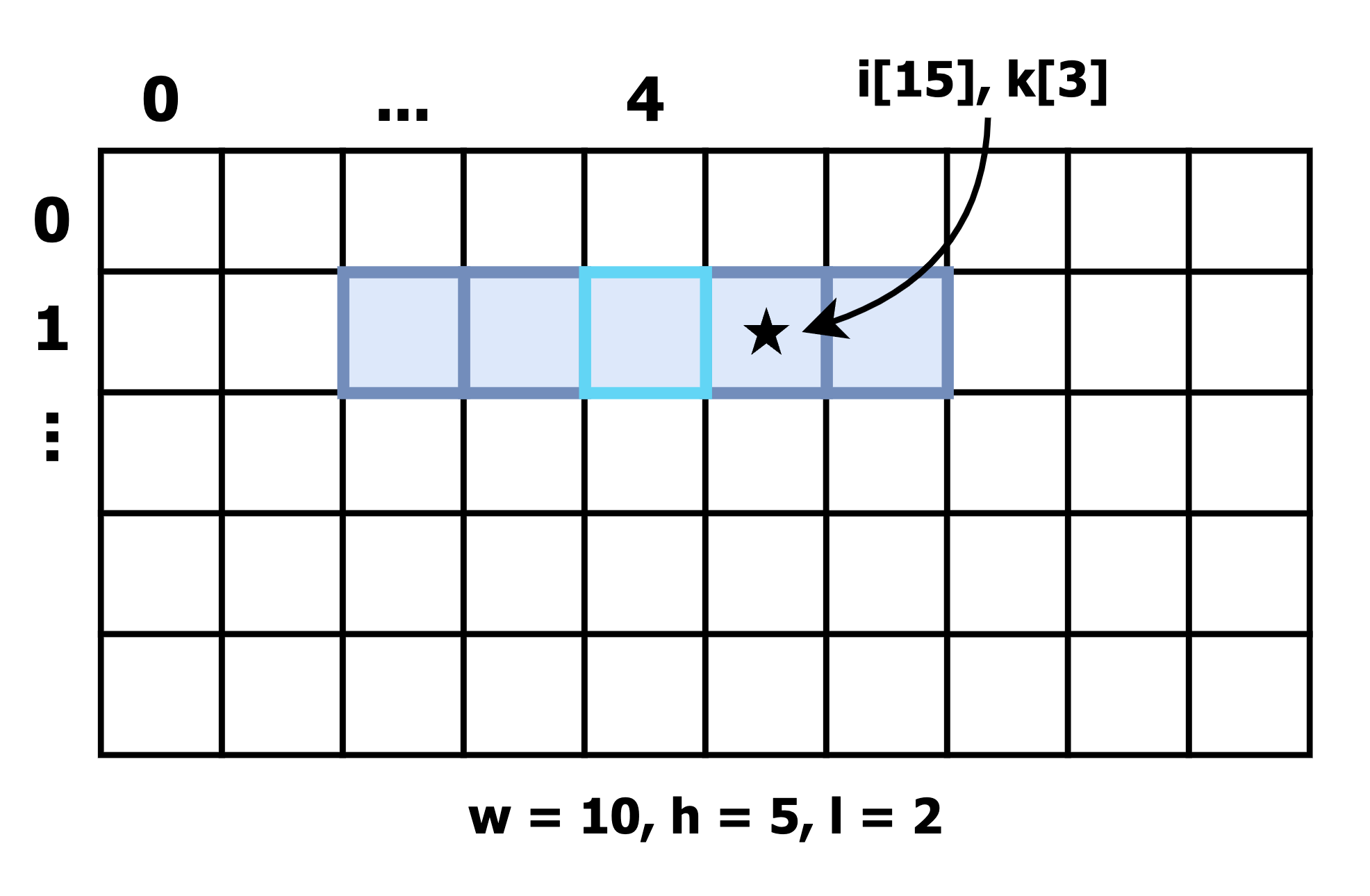
Suppose that you are given a 1D image vector
Write out pseudocode to slide the kernel
How would you need to adjust this pseudocode if the kernel were positioned vertically instead?
Answer:
For horizontal convolution, the pseudocode might look like this:
for each row in the image...
for each column in the image...
for each element in the kernel...
find the row and column of the current pixel:
row = current row
column = current column + element index - kernel radius
use row and column to find the index in the 1D image vector
...
Duality of Domains
Visualizing Sinc and Box Duals
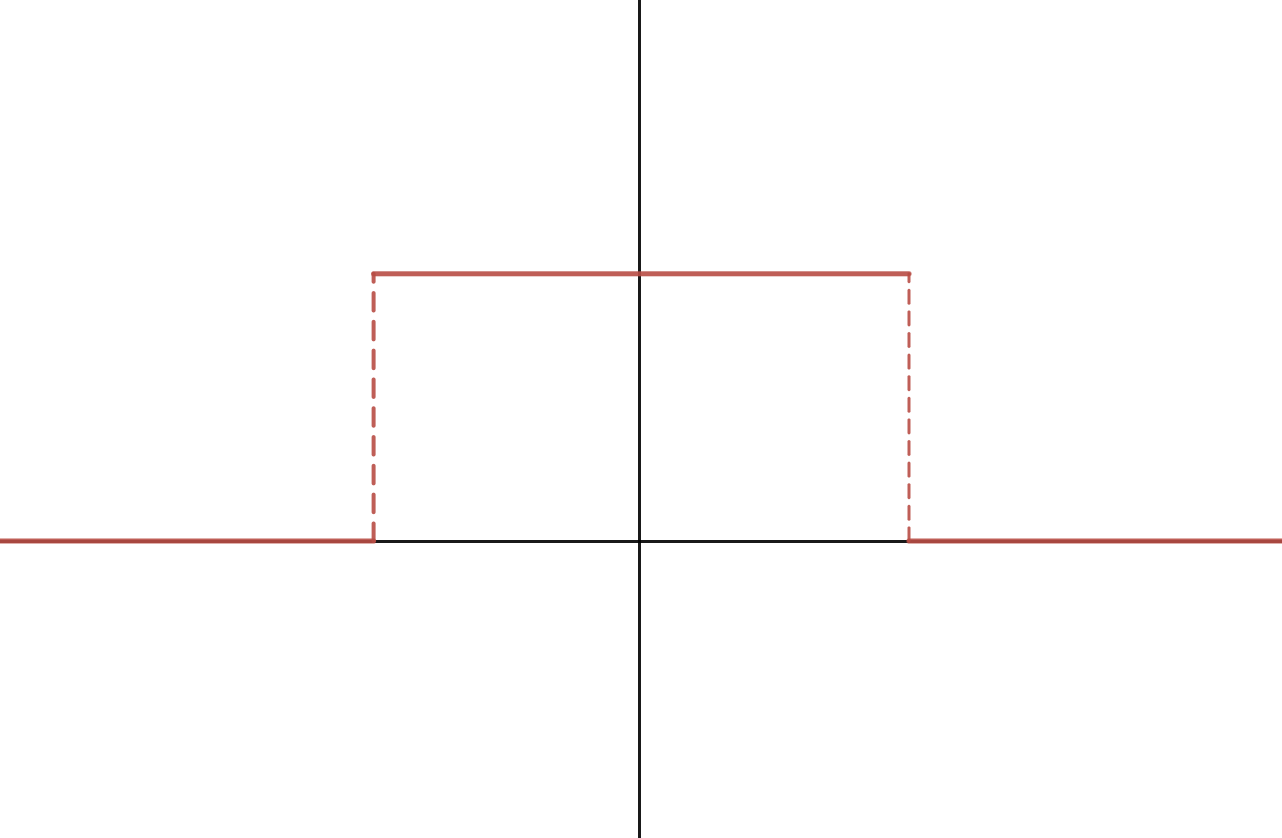
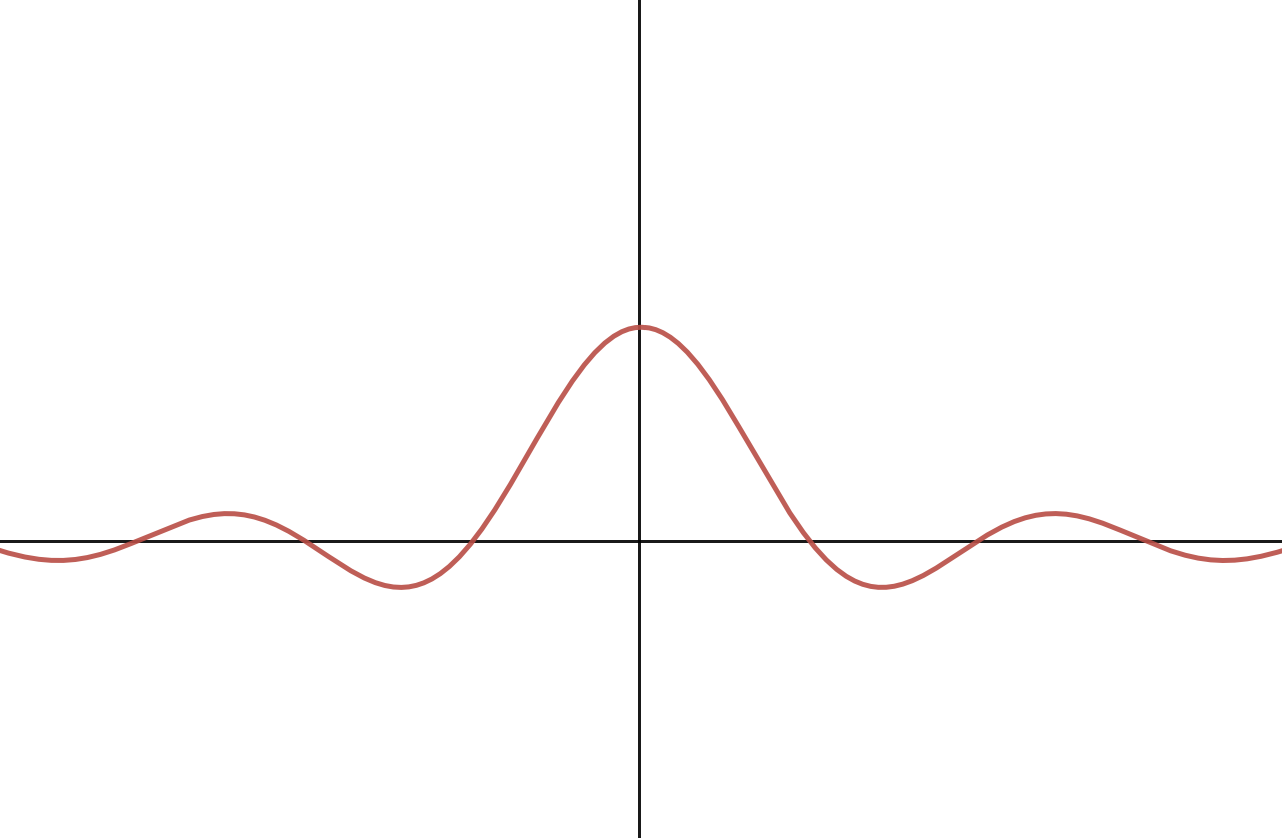
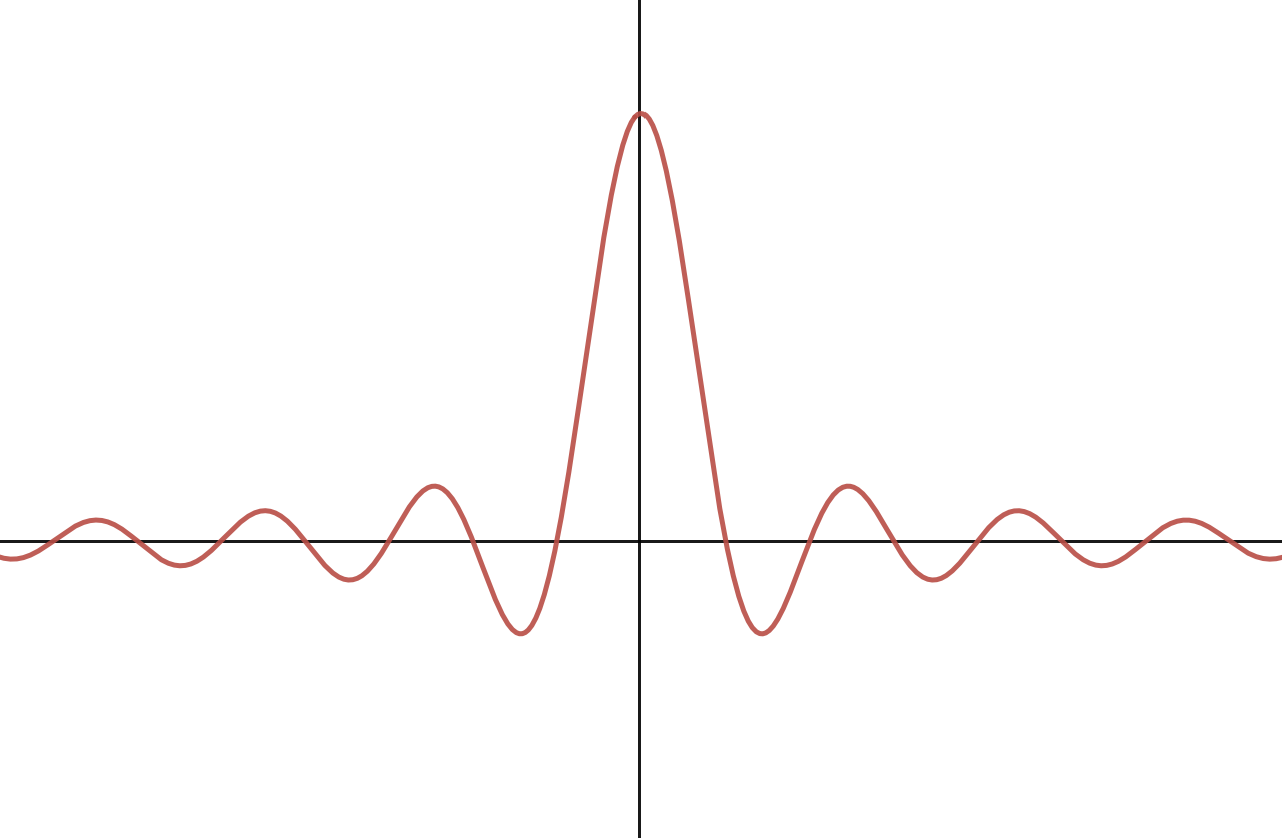
Take a look at the box function in figure 5 (left) below. Its dual in the frequency domain is the sinc function, in figure 5 (right). Note that there are no labels on the axes, by design.
Draw out a sketch of the dual of the box function in figure 6. Your drawing doesn't need to be perfectly accurate; but enough to show that you understand the concept.
When you are finished, explain your group's thought process to the TA.
Answer
Explanation:
A wider box function in the frequency domain means that there are more signals with higher frequency. To reflect this fact in the spatial domain, the sinc function needs to have higher frequency, or, oscillate more. Visually, the sinc function becomes narrower.
Approximating Sinc
What do we usually use to approximate the sinc function, and why do we have to make this approximation when translating these theoretical concepts into code?
Discuss with your group and then call over the TA to check your understanding.
Answer
A Gaussian function. Though, in cases where the approximation doesn't have to be as good, a triangle function can be used instead.
Explanation:
Both the Gaussian and triangle filters are cheaper to use.
Sinc functions are infinite in extent, and it's simply not feasible to perform discrete convolution with an infinitely large, nor would it be performant to approximate it with a "very large" one.
Gaussians are technically also infinite in extent, but fall to almost-zero fairly quickly. Thus, Gaussians can be used as a cheaper approximations to the sinc filter. Compared to the triangle, it also has a nice property: a Gaussian's dual in the frequency domain is another Gaussian, which means it better approximates a good low-pass filter.
Sampling in the Frequency Domain
If we're sampling a continuous function at a frequency of
Answer
Any frequency less than, but not equal to
Explanation:
In order to capture all frequencies in a signal, we must sample at a rate that is strictly higher than 2 times the highest frequency. Thus, if are sampling
Frequency Plots
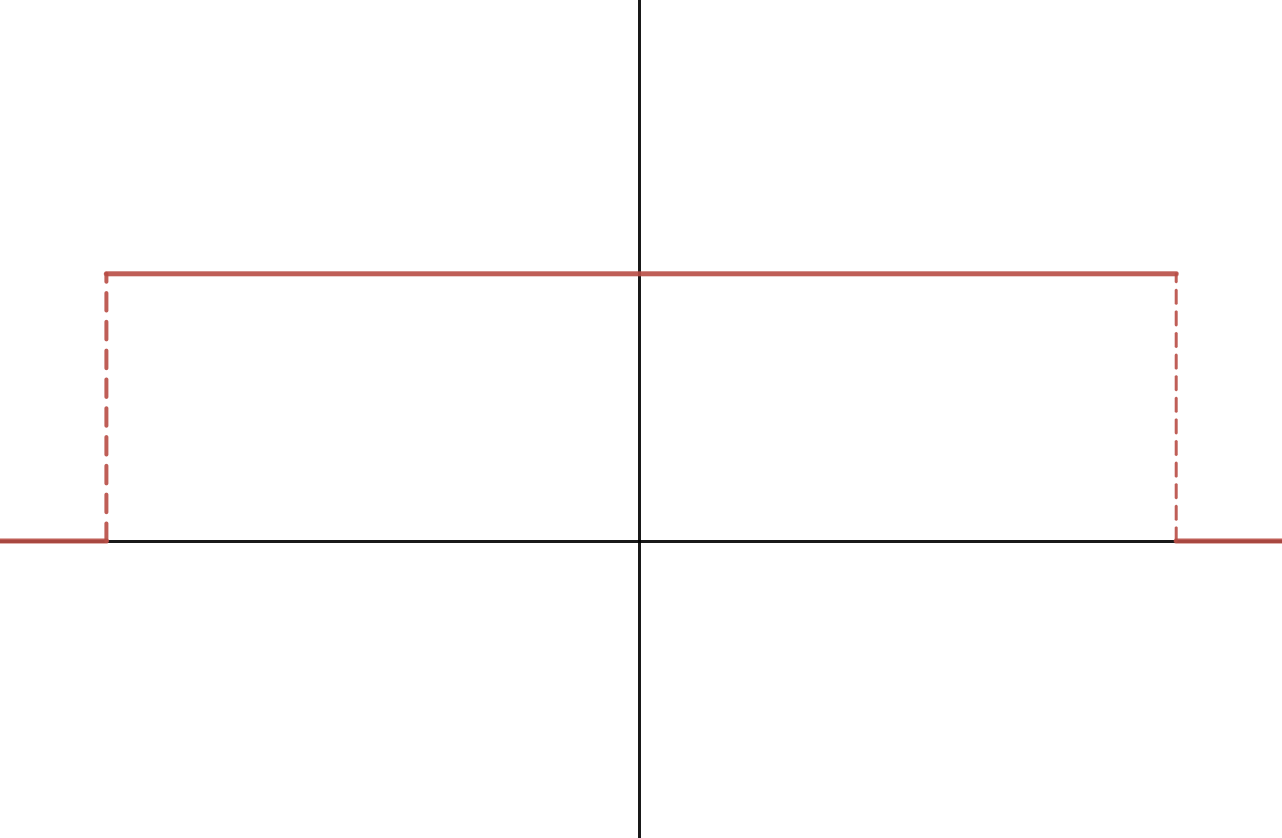
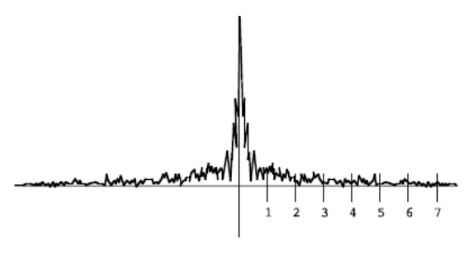
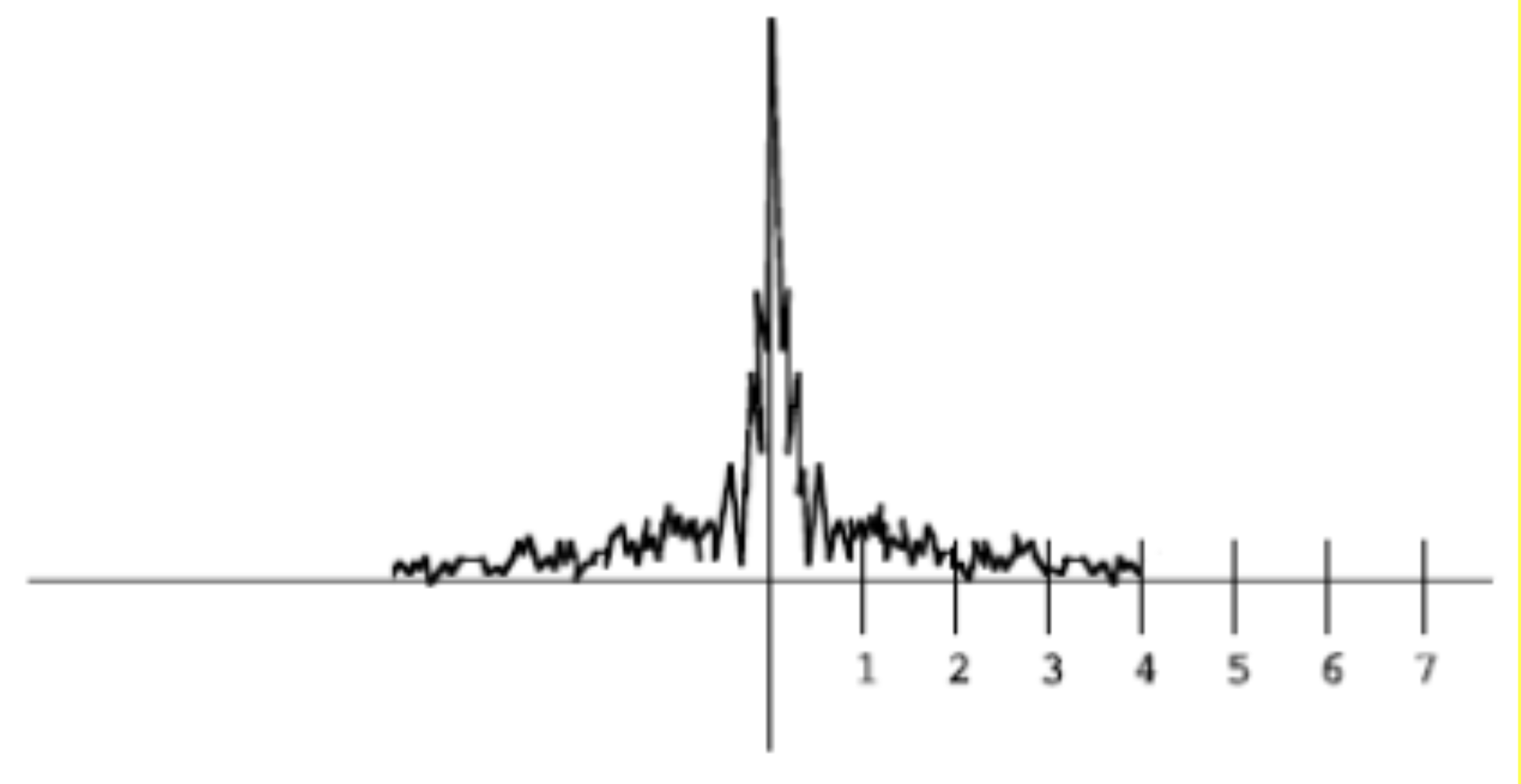
Now, examine the following frequency plot of a 1D, continuous signal. If you were going to sample this signal at a rate of 8 samples per unit, to avoid aliasing, you would use what we know about the Nyquist limit to pre-filter it.
Draw out the new frequency plot after someone has performed this pre-filtering step optimally. Make sure to include any relevant amplitude and/or frequency values.
Answer
Explanation:
To avoid aliasing, we need to prefilter the signal by running a low-pass (blur) filter to eliminate high frequencies. In the frequency domain, if we want to eliminte frequencies higher than
In our case, since we are sampling the signal at 8 samples per unit, we can only represent functions with frequency lower than 4. Thus, the box function centered around 0 should have width
Ray Differentials for Spheres
Review: Texture Coordinates
Recall that we can express coordinates on the surface of a sphere using spherical coordinates
Answer:
From Object to Texture Space
Using the equations that we found in 3.1 and the definition of
Answer:
We can plug:
And solve for:
Calculating Differentials
Calculate
The following derivatives might be helpful:
Answer:
For
For
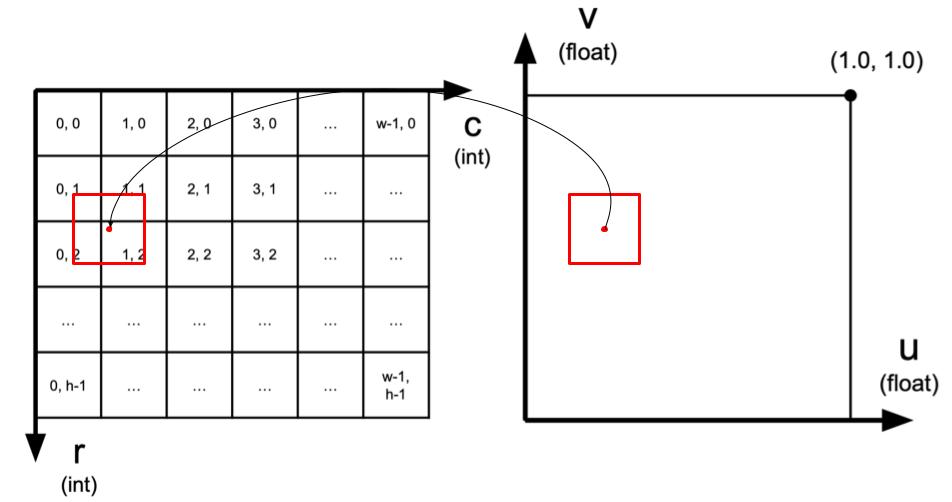
Bilinear Sampling
Suppose we have texture of size
Answer:
We need to find the 4 pixels surrounding the point
Submission
Algo Sections are graded on attendance and participation, so make sure the TAs know you're there!